The Esophageal and Stomach Cancer Program at Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi brings together a multidisciplinary team of gastroenterologists, oncologists and surgeons. Using the most sophisticated diagnostic tests, our team works together to provide an individualized care plan for each patient.
Esophageal and stomach cancer can affect swallowing and therefore impact quality of life. Therefore, we work alongside a team of supportive services, including nurses, pain management specialists, social workers and dieticians.
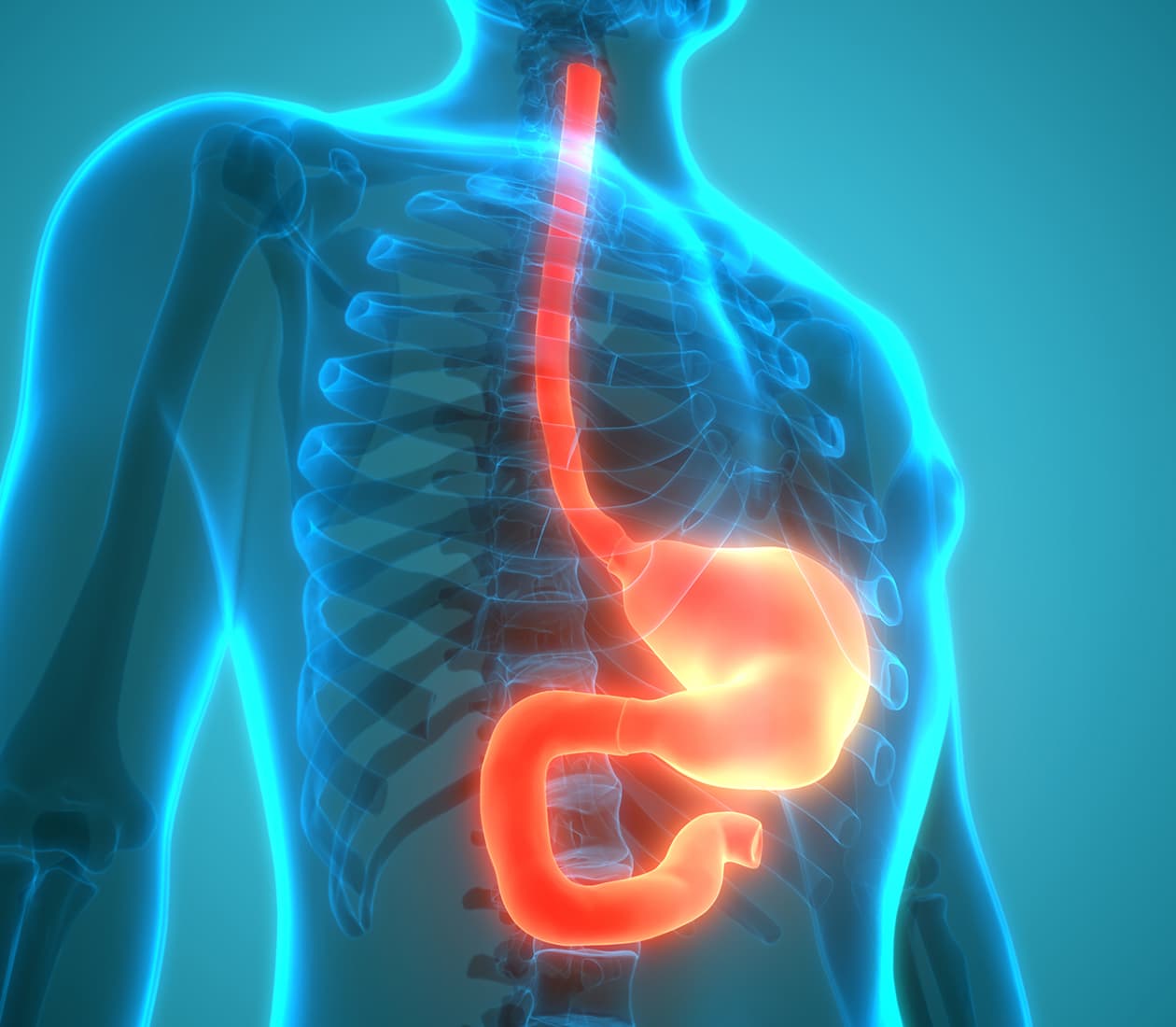
We work in close collaboration with the Cleveland Clinic US’s esophageal cancer program, working together to explore the best medical and surgical options to ensure the most successful outcome for each patient.
Our multidisciplinary tumor board meets weekly to review each patient case individually. Specialists in thoracic and gastrointestinal cancer sit together to discuss clinical management decisions and tailor treatment plans to their patients’ needs, seeking to further improve cancer care. This tumor board and multidisciplinary approach to total care means our patients get the benefit of several expert opinions for their diagnosis, treatment, and overall care. We also work closely with the patient and their family to provide the best chance of cure with a focus on improving quality-of-life.

The Esophageal and Stomach Cancer Program treats the following conditions:

Signs and symptoms of esophageal cancer can include:
Signs and symptoms of stomach cancer can include:
Doctors don’t know what exactly causes esophageal and stomach cancer but there are several factors that might put you at an increased risk of developing either disease.
When the cells in the esophagus or stomach develop changes (mutations) in their DNA which cause them to divide out of control, it leads to cancer. These changes cause abnormal cells to accumulate and form a tumor, which can invade nearby structures and spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body.
It is thought that persistent irritation in the esophagus might lead to changes which cause esophageal cancer. Factors that cause irritation include:
Factors that increase your risk of developing stomach cancer include:

Tests and procedures used to diagnose esophageal and stomach cancer include:
Once a diagnosis confirms cancer, your doctor may perform further tests to determine the stage of the cancer and the most appropriate type of treatment. These tests might include:
Treatment will depend on the type of cancer you have, where the cancer is located, its stage and your overall health and treatment preferences.

There are things you can do to reduce your risk of esophageal and stomach cancer, including:
Talk to your doctor about your risk of developing esophageal and stomach cancer. If you have a strong family history of either disease, they may recommend tests, such as endoscopy, to look for early signs.

Caregivers supporting the Esophageal and Stomach Cancer Program include:

Speak with our Contact Center for assistance
Request an Appointment 800 8 2223 International Patients