
The Ovarian Cancer Program at Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi’s Cancer Institute provides care for women during what can be a very difficult time. Combining the very latest diagnostic and treatment techniques, supported by highly specialized and compassionate care, is an important differentiating factor when treating ovarian cancer and an essential part of improving outcomes for patients.
We offer a truly collaborative approach to cancer care, close to home. Our team of specialists excel in numerous advanced diagnostic and treatment methods, combining cutting-edge technology with compassionate treatment approaches. The team also works hard to raise awareness about ovarian cancer, providing proactive prevention methods with the availability of top-tier medical care at Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi.
The Ovarian Cancer Research Alliance states, “According to numerous medical studies, there are significant survival advantages for women who are managed, operated on and treated by a gynecologic oncologist. Gynecologic oncologists are five times more likely to completely remove ovarian tumors during surgery.”
Our multidisciplinary team is led by one of the region’s only female Gynecologic Oncologists, Dr. Stephanie Ricci. She is a specialist in the treatment of female cancers, and one of only a handful in the UAE. Treatment for ovarian cancer by a gynecologic oncologist is extremely important as they have the dedicated training, specialist experience and technical skills needed to diagnose and treat the cancer as effectively as possible. Dr. Ricci is a fellowship trained, American board-certified and spent 6 years at Cleveland Clinic in the US. She has dedicated her career to helping women affected by cancer.
Our multidisciplinary approach brings together a team of experts to provide coordinated and exceptional patient care to those diagnosed with gynecologic cancers. The team meets regularly as a multidisciplinary tumor board to discuss each patient and ensure the best treatment options are considered for each individual.

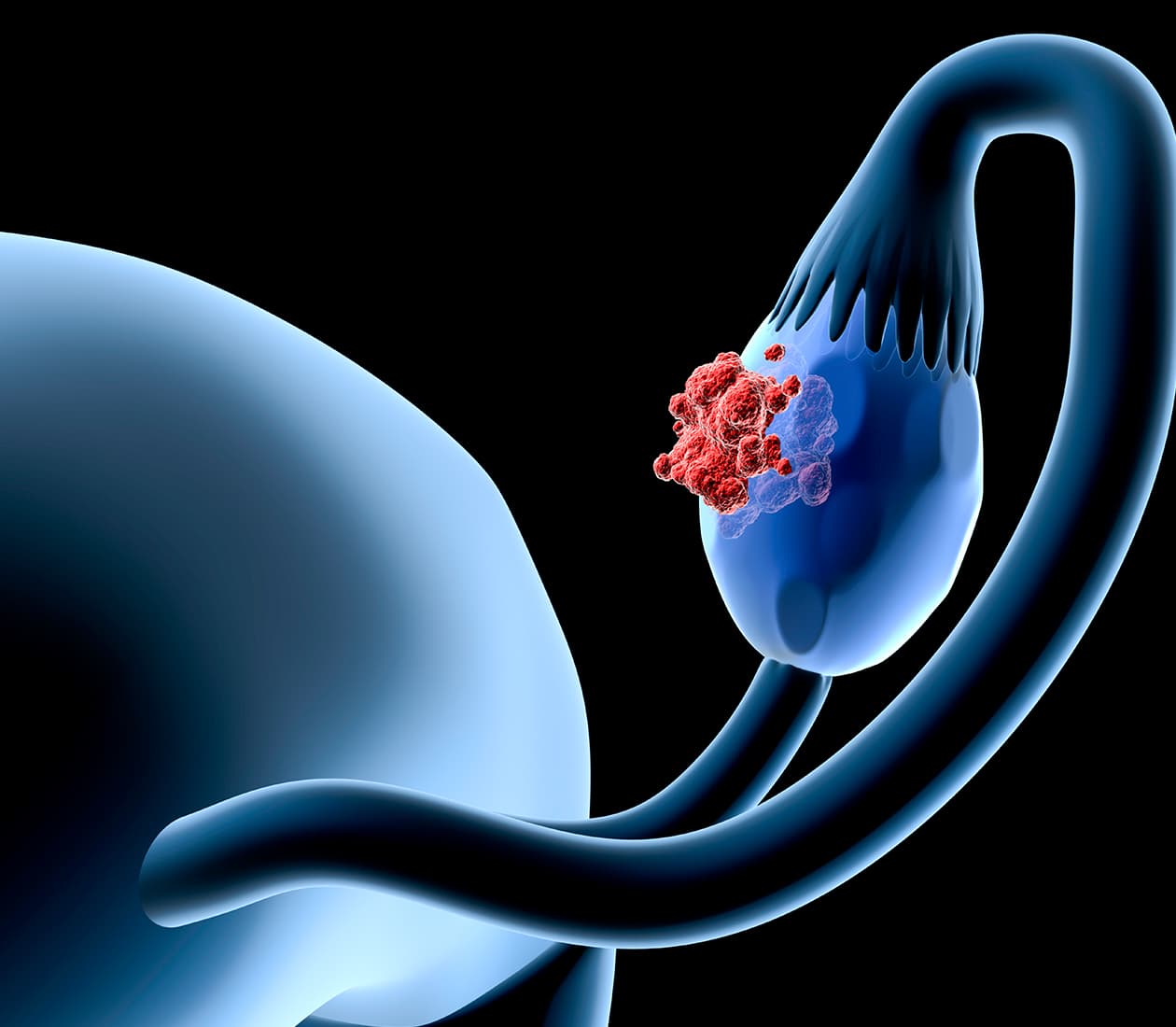
Ovarian cancer is the abnormal growth of cells within the ovaries – the part of the female reproductive system that makes eggs. This abnormal growth can lead to the formation of a tumor, which can be benign (not cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Benign tumors may not pose a problem to your health, but malignant tumors are more aggressive and can spread to other parts of the body. Ovarian cancer symptoms often don’t appear until the disease is at a more advanced stage.
The team of specialists at the Ovarian Cancer Program at Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi are highly trained in a variety of diagnostic techniques and state-of-the-art therapeutic treatments for ovarian cancers.

Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer often has no symptoms until the later stages, when it may have spread through the abdomen. Ovarian cancer symptoms might include:
Causes & Risk Factors of Ovarian Cancer
Doctors don’t know the exact cause of ovarian cancer, but there are certain risk factors that put you at an increased risk. These include:

Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer
Unfortunately, there are no screening tests available for ovarian cancer and testing usually happens once symptoms are present. Therefore, it is important to notify your doctor as soon as you notice something that is unusual for you.
Your doctor will begin by discussing your medical history and performing a physical exam. A pelvic exam will look for any lumps or enlarged organs. If your doctor feels additional tests are needed, these might include:
Treatment for Ovarian Cancer
Treatment of ovarian cancer aims to remove as much of the cancer as possible. This usually means removing any organs (or part of the organ) that the cancer has spread to.
Learn more about the advanced treatment options available for ovarian cancer here.
After you have received treatment for ovarian cancer, you will need to see your doctor regularly to discuss any possible symptoms and to check the cancer hasn’t returned. Observation following ovarian cancer is very important.

Ovarian cancer can’t be prevented and unfortunately there are no screening tests for it. However, there are things you can do to decrease your risk of getting cancer as you get older, such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating well and exercising regularly.
Being aware of your family history is also important. Studies have shown that women who have had children or have used oral contraceptives for more than 5 years are less likely to develop ovarian cancer.
There are two gene mutations associated with ovarian cancer, known as BRCA1 and BRCA2, which are also associated with breast cancer. If there is a strong family history of either of these cancers, your doctor may suggest genetic testing to identify these mutations. Breakthroughs in genetic testing for mutated BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes offer significant advancements in personalized risk assessment and treatment. Understanding a patient's genetic predisposition to ovarian cancer aids in tailored screening strategies and targeted therapies. If there is a strong family history of ovarian cancer, your doctor may suggest genetic testing to identify these mutations. This can help identify a cancer prevention strategy.

Our female-only, multidisciplinary team of caregivers includes:

Speak with our Contact Center for assistance
Request an Appointment 800 8 2223 International Patients